How is the leasing market performing in the current economic environment?
Positioned between crisis and resilience
Rising interest rates, geopolitical uncertainties and an investment backlog of over EUR 600 billion are currently shaping Germany’s economic landscape.[1] Many companies are holding back, postponing investments – traditional financing models are increasingly coming under pressure.
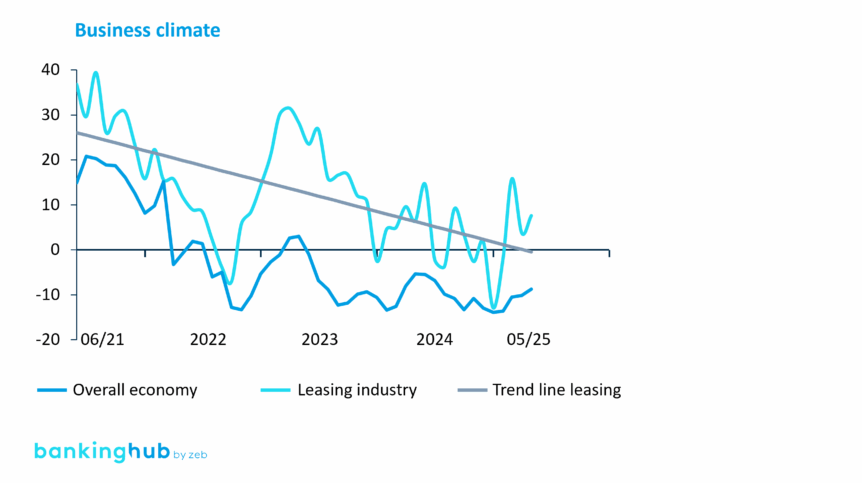
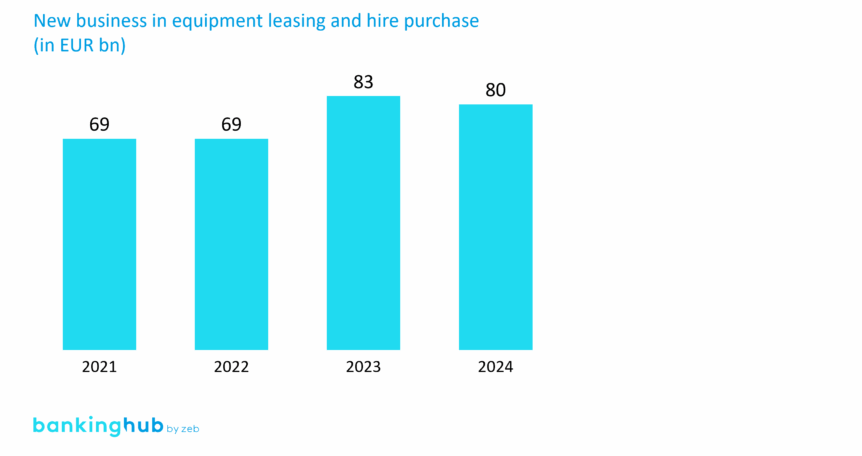
Despite the strained economic climate, the leasing market remains remarkably stable. Since mid-2021, the ifo Institute has reported a significant decline in overall economic sentiment, including in the leasing industry. However, this has only had a limited impact on new business in equipment leasing and hire purchase.[2] The volume has grown – from EUR 69 billion in 2021 to around EUR 80 billion in 2024.[3]
This trend highlights the industry’s resilience. Leasing is increasingly being used as a strategic financing tool – not just to bridge funding gaps, but to enable essential investments in energy, heating, mobility and education.
Especially in times of stagnant investment, leasing offers clear advantages: It eases liquidity pressure and offers off-balance sheet financing, as well as allowing for flexible terms. This makes it an attractive model, particularly for mid-sized companies and public institutions.
How is the leasing market changing?
From cars to a broader mix
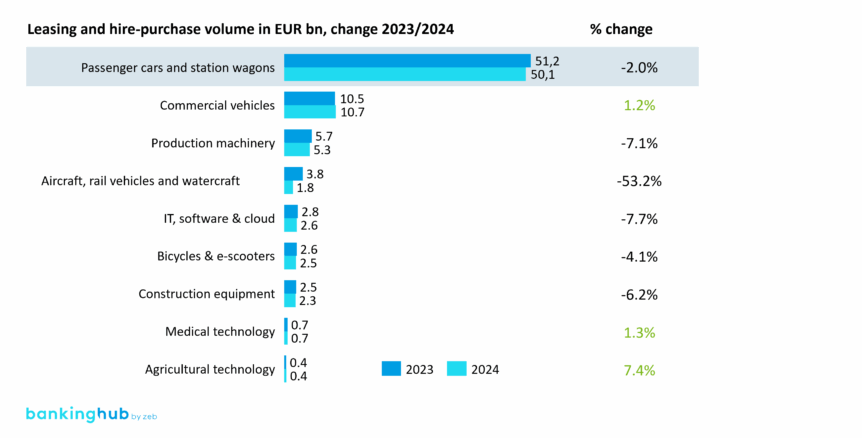
When looking at the leasing market, one segment consistently takes center stage: vehicle leasing. At first glance, it still clearly dominates – about 80% of new business volume currently comes from vehicle leasing. But momentum is slowing: after growing by 22.5% between 2022 and 2023, the passenger car and station wagon segment declined by 2.0% in 2024. These figures suggest a potential trend reversal and bring structural challenges into sharper focus.
The structural challenges in the vehicle segment are multifaceted: Demand for battery electric vehicles (BEVs) – a leasing favorite – has dropped by over 27% since government subsidies were withdrawn.[4] At the same time, new players – especially from China – are entering the market with competitively priced models. While their market share is still below 2%, there’s a real risk of market share shifting at the expense of German OEMs in the long run.[5] Mobility preferences are also changing: the number of car-sharing vehicles has risen by 72% since 2020, and the number of passengers using local public transport is also climbing again.[6] This shows: traditional private car ownership is losing its status as the default –along with the conventional business model of vehicle leasing.
Why is a 9.5% increase in efficiency necessary?
Cost pressure in the leasing market
These developments are putting noticeable pressure on the vehicle leasing business. According to zeb’s calculations, stagnant growth, intensified competition, residual value risks and rising operating expenses – such as labor and interest costs – are creating an average cost pressure of around 9.5%, which must primarily be offset through operational efficiency.
Independent leasing providers can respond more flexibly to market shifts, while captive finance companies face greater challenges in stabilizing their sales channels – often through subsidies or special offers.
BankingHub-Newsletter
Analyses, articles and interviews about trends & innovation in banking delivered right to your inbox every 2-3 weeks
"(Required)" indicates required fields
What’s the strategic rethink needed for leasing?
Rethinking the business portfolio
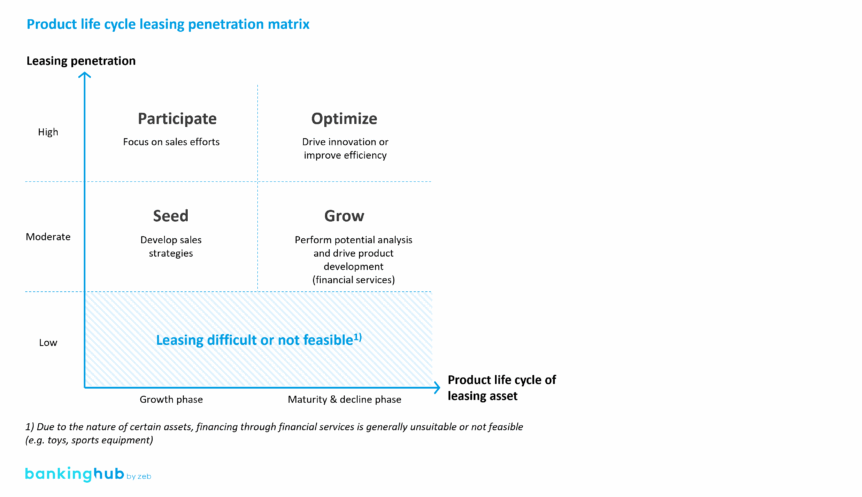
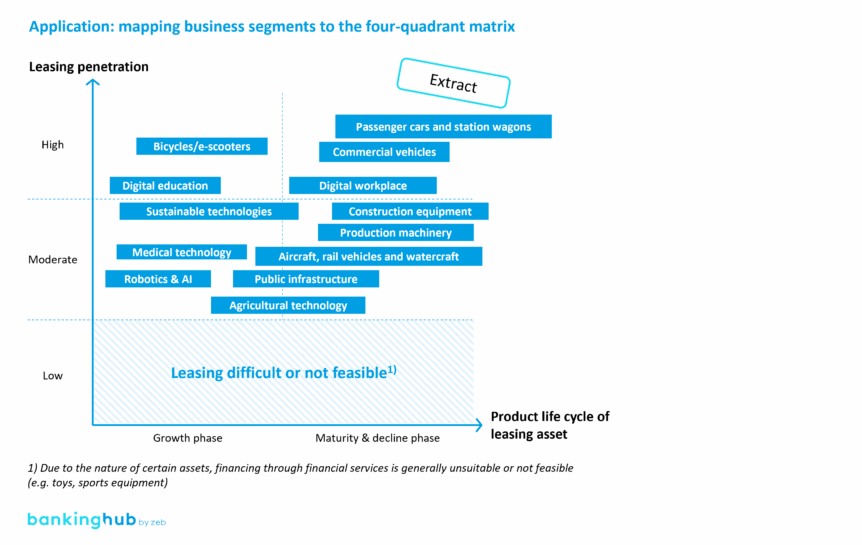
The structural transformation of the leasing market calls for a new approach to portfolio management. The previous focus on a few dominant asset classes – especially in the automotive sector – is no longer sufficient. Instead, companies need to assess their product portfolios along two key dimensions: the product life cycle of the leased asset and the market penetration of leasing as a financing method.
zeb analyzes these dimensions using a four-quadrant matrix that categorizes business segments based on their maturity and leasing penetration. The objective: identify areas for action and derive generic strategic approaches to guide portfolio development.
Overview of generic strategic approaches
- Grow: business areas with high potential and strong leasing penetration (e.g. construction and production machinery) – zeb approach: scale operations and expand market reach.
- Participate: segments with moderate penetration and high maturity (e.g. bicycles and e-scooters) – zeb approach: optimize sales and improve efficiency.
- Seed: emerging markets with strong future potential (e.g. agricultural technology, robotics) – zeb approach: invest in development and build internal expertise.
- Optimize: mature markets with declining momentum (e.g. traditional vehicles) – zeb approach: lead in cost efficiency and strengthen customer loyalty.
How leasing providers can shape the transformation
Actionable recommendations for leasing providers
The transformation of the leasing industry is not a future scenario – it is already underway. Providers must rethink their business models and go-to-market strategies to stay competitive. The challenges are complex: The interest rate reversal of recent years has significantly increased refinancing costs, while growth in the vehicle segment has stalled. New entrants, especially from abroad, are intensifying price competition. Subsidy programs are ending, margins are tightening, and customer mobility habits are clearly shifting. In addition, a fragmented market environment is also raising the bar for product differentiation, sales efficiency, and strategic management.
Against the backdrop of current market changes, zeb identifies four key areas for action:
- Refine the portfolio:
Invest in asset classes with growth potential – such as sustainable technologies, medical equipment, or digital infrastructure – to unlock new opportunities. At the same time, manage mature, low-margin segments with maximum efficiency. - Strengthen governance and control capabilities:
New markets require new skill sets. Systematically assess profitability by business segment – using tools like the zeb.cost.engine – to gain a competitive edge. - Increase cost efficiency:
According to zeb’s calculations, an average cost reduction of around 9.5% is necessary to offset the adverse effects of rising costs and interest rates. - Extend the value chain:
Leasing as a standalone financing product is no longer enough. Additional services – such as maintenance, insurance, or usage-based billing models – combined with smart data utilization, create real added value and boost customer loyalty. Leasing providers should expand their offerings into comprehensive usage packages.
Where is the leasing industry heading?
The leasing industry proves its resilience in a challenging economic environment
And even more: it has the potential to emerge from the crisis as a winner. However, this requires a clear strategic focus and the ability to actively shape change.
Now is the time for leasing providers to realign their structures and seize the opportunities of transformation. With its deep expertise in the leasing business, zeb is well-positioned to support this transition.