How did the yield curve evolve from 2012 to 2024?
Before venturing into the depths of interest rate risk management, let’s take a brief look at developments over the past few years.
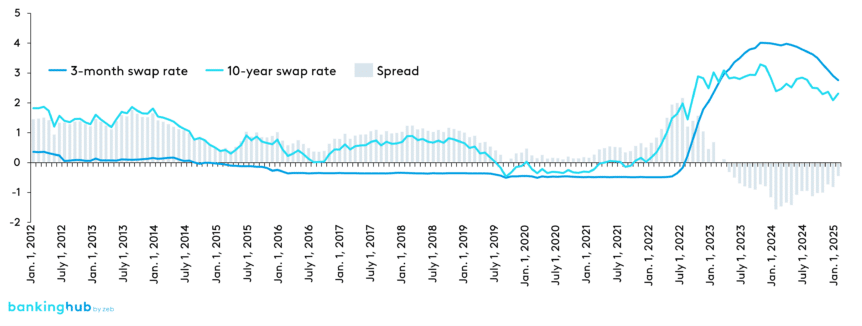
Figure 1 shows the evolution of money and capital market interest rates using a 3‑month and a 10‑year swap rate, as well as the term spread between the two rates. The spread indicates the benefits of interest maturity transformation.
The low interest rate phase from 2012 to 2022, characterized by steadily declining interest rates and a negative interest rate environment from 2019 onwards, is clearly visible. As of 2022, we can obverse the rapid rise in interest rates due to ECB policy and the resulting inverted yield curve (negative spread).
Looking back: what impact did the interest rate phases have on German regional banks?
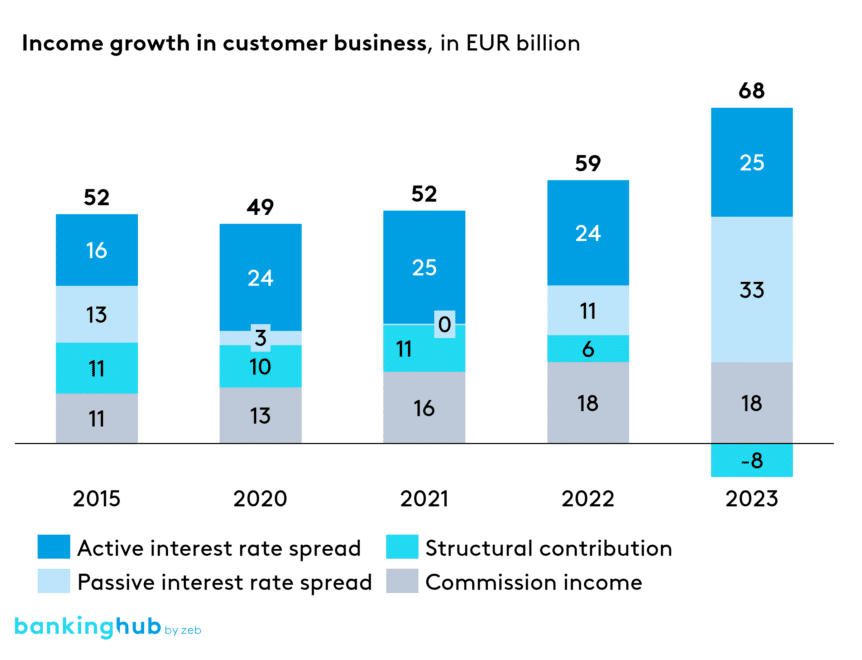
Before the low interest rate phase, German regional banks’ income typically consisted of four elements roughly equal in percentage: active net interest spread, passive net interest spread, commission income and structural contributions. This earnings mix, still evident in 2015, has changed significantly over the years, as shown in Figure 2 [1] below.
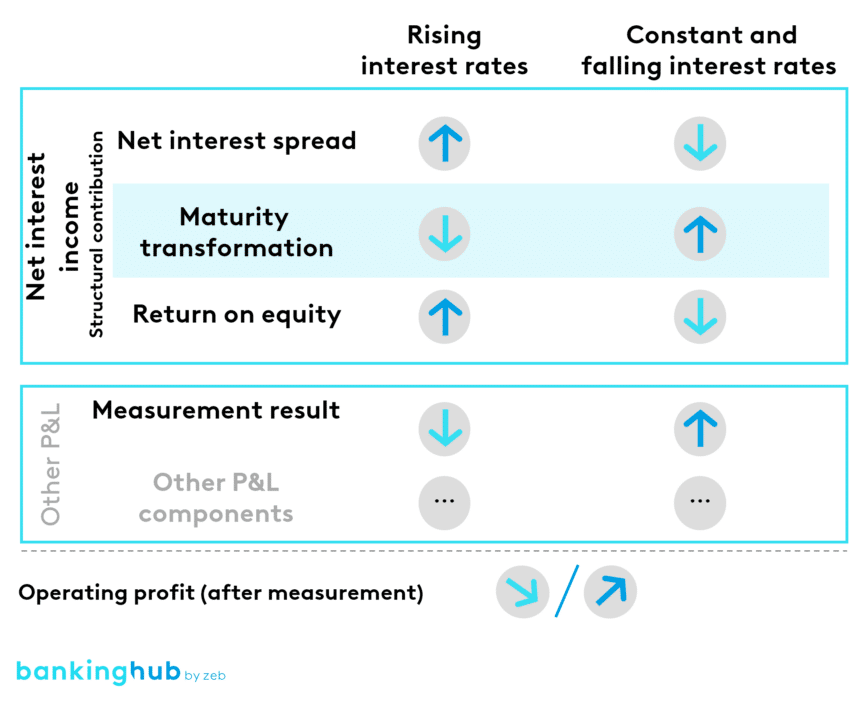
The shift in the earnings mix stems from different interest rate phases. Figure 3 illustrates the underlying “effect mechanism”. Declining interest rates generally have a negative impact on net interest spreads and return on equity.
On the other hand, there was a positive impact on valuation results and maturity transformation. The overall effect depends on the bank’s business model and balance sheet structure. Rising interest rates have the opposite effect.
Let’s examine a regional bank that has passively positioned its interest rate book based on a “2 × 10‑year moving average”[2] structure to illustrate the effects of interest rate phases from maturity transformation.
- Low interest rate phase (2012–2022): During the period of low and negative interest rates, many banks generated a significant portion of their net interest income through maturity transformation to compensate for low margins on liabilities from customer business. This strategy allowed many German regional banks to generate a stable stream of income by benefiting from the steepening of the yield curve and the overall drop in interest rates resulting from the rapid decline in the short end.[3] During this phase, our model bank benefited considerably from its interest book positioning and was able to build valuation reserves in the interest book (rising present value). Net interest income remained roughly constant, margins narrowed, while the transformation result had a stabilizing effect.
- Rapid rise in interest rates (2022–2023): The sudden and significant rise in interest rates starting 2022 posed considerable challenges. Many savings banks and German regional banks were exposed to high present value interest rate risks, and previously accumulated economic reserves rapidly lost value. In addition to write-downs in the securities area, which had a negative impact on the income statement, provisions for the loss-free valuation of the banking book also had to be recognized in the income statement in some cases. The opportunities created by the low interest rate environment in the interest book led to substantial charges. Our model bank would have fared better had it entered this phase with significantly lower interest rate risks. However, the purely passive management approach lacked the necessary flexibility.
- Inverted yield curve (since 2023): The ongoing phase of the inverted yield curve has resulted in strongly negative maturity transformation contributions for other “short vs. long” maturity transformation positions. This constellation has forced many banks to reassess their strategies. By December 2024, the 10‑year swap rate was still well below the 3‑month swap rate (see Figure 1). This scenario necessitates a differentiation between sales and treasury contributions to manage planned interest surpluses. Our model bank is now faced with the challenge of deciding how to manage the interest rate risk position in the future, as an inverted yield curve also results in losses in a passive benchmark strategy.
Analyzing individual interest rate phases reveals that a proactive approach is essential not only for minimizing risks but also for capitalizing on opportunities. Purely passive interest book management falls short in volatile interest rate markets and should be reconsidered.
But how can German regional banks apply this insight to their future strategy? One possible solution is scenario analysis, which explores potential developments and their impacts on the interest book.
BankingHub-Newsletter
Analyses, articles and interviews about trends & innovation in banking delivered right to your inbox every 2-3 weeks
"(Required)" indicates required fields
Looking ahead: what implications can be derived from standard interest rate scenarios?
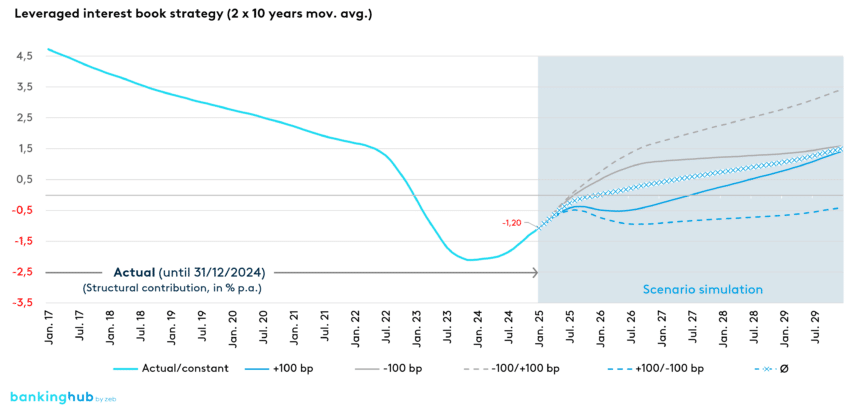
We again use our model bank to project future scenarios. The positioning of the interest book (2 × 10‑year moving average) clearly indicates that a return to positive interest contributions is only possible with a significantly steeper yield curve in the coming years (see Figure 4 4]).
Overall, the scenarios suggest that the structural contribution in the “2 × 10‑year moving average” strategy is likely to recover by 2026
It is evident that a purely passive interest book strategy no longer meets the requirements of today’s volatile market. Excessive risk and lack of flexibility to respond to changes necessitate a reevaluation.
To thrive in a dynamic market, German regional banks must transition from a passive to a semi-active interest book management strategy. This approach enables targeted responses to new market situations and proactive risk management, rather than merely mapping risks. Benchmark mapping alone is insufficient; flexible management is crucial to capitalize on earnings opportunities as well as to minimize risks.
What are the consequences for the further development of interest rate book management?
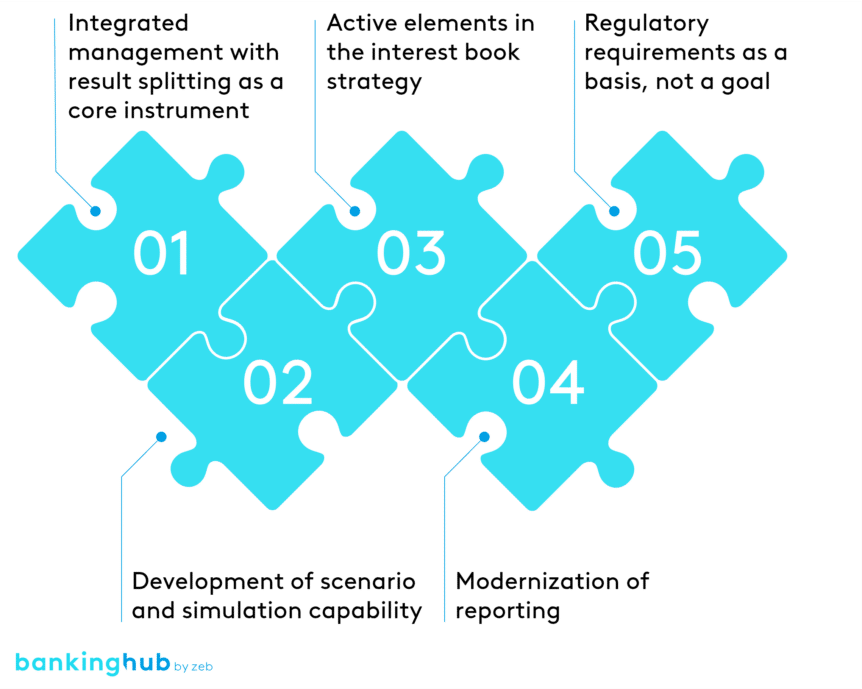
In our view, the areas for action need to be clearly prioritized. We identify five central areas for action:
I) What is the significance of integrated management with income splitting in interest book management?
MaRisk already requires banks to separate net interest spread and structural contributions. However, as the illustrations above have shown, the use of the key figures also makes sense from a management perspective. This means that measures such as reducing or increasing the transformation position in times of rising and falling interest rates can be considered.
Why is this important? Only by taking a differentiated view of the sources of income can banks manage their income and risk potential in different interest rate phases in a targeted manner.
What needs to be done? Banks should develop an integrated management approach that combines both economic and P&L perspectives. Management must aim not only to limit risk, but also to actively optimize returns.
II) Why is scenario analysis and simulation capability so important for interest rate book management?
Interest rate movements are highly volatile and can rarely be accurately predicted. Nevertheless, scenarios and simulation models can help to identify trends and the potential effects of different market conditions. The aim is not so much to make precise predictions, but rather to gain a profound understanding of how different developments might affect the earnings situation and risk structure.
Why is this important? Simulation capabilities make it possible to identify potential developments at an early stage and to take advantage of opportunities in a timely manner.
What needs to be done? Banks are recommended to implement and fully utilize modern simulation and forecasting tools that can accurately depict various interest rate trends and their impact on earnings.
III) Which active elements should be integrated into an interest rate book strategy?
The interest rate scenarios described make it clear that purely passive strategies are no longer appropriate in volatile markets. Incorporating active elements (“guard rails around the target image”) into the management system provides the necessary flexibility to take advantage of short-term market opportunities, such as sudden interest rate rises, and to respond effectively to changes in the interest rate structure.
Why is this important? Banks can only exploit short-term market opportunities and minimize losses in adverse scenarios through more active management along a rule-based process (rather than “gut decisions”).
What needs to be done? It is prudent for banks to implement a set of management tools that enable rule-based decisions, and train managers to use these tools effectively.
IV) What is the role of modern reporting in interest book management?
Modern reporting is critical for making informed decisions in volatile markets. Enhanced dashboards and accurate KPIs create transparency and provide managers with the data they need to react quickly to interest rate changes. Long reporting cycles or only partial data updates, such as those permitted by the supervisory authorities for small banks (“small banking box”), must be critically examined, as decisions need to be made quickly, especially during volatile market periods, to avoid being left behind.
Why is this important? Modern reporting creates transparency and improves the quality of decision-making – especially in crisis situations.
What needs to be done? Banks ought to enhance existing systems to provide more granular and timely information on revenue streams.
V) How should German regional banks deal with regulatory requirements in the context of interest rate book management?
Compliance with regulatory requirements, such as BFA3 (Statement on the loss-free measurement of the interest book, Banking Committee of the Institute of Public Auditors in Germany, IDW) or interest rate risk ratios, is essential, but should not be the sole focus.
Why is this important? Regulatory compliance is the foundation for sustainable business, but it must not stifle innovation.
What needs to be done? Banks must ensure that regulatory requirements are integrated into management approaches without compromising the bank’s flexibility.
The combination of strategic income splitting, advanced simulation tools and flexible interest book management will determine who succeeds in a volatile interest rate environment.
Net interest income splitting is more than just a technical management tool. Those who act proactively today – by expanding simulation capabilities, managing results in a more sophisticated way and modernizing reporting – will not only minimize risk, but also develop sustainable revenue streams. The message is clear: act now to be successful tomorrow.