How successful was 2023 for Austrian regional banks?
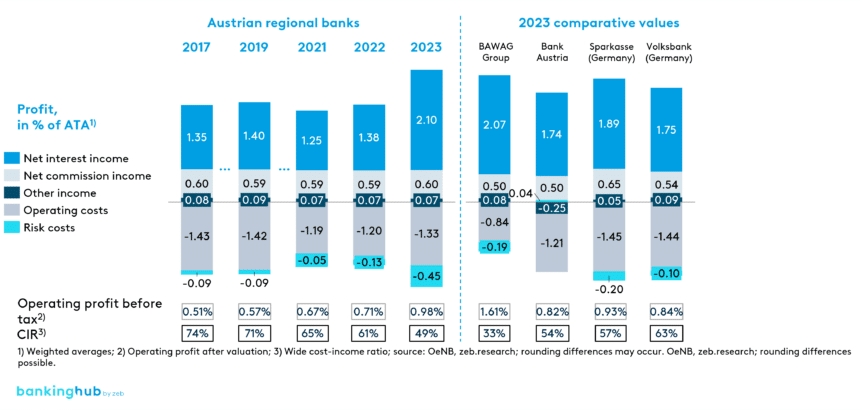
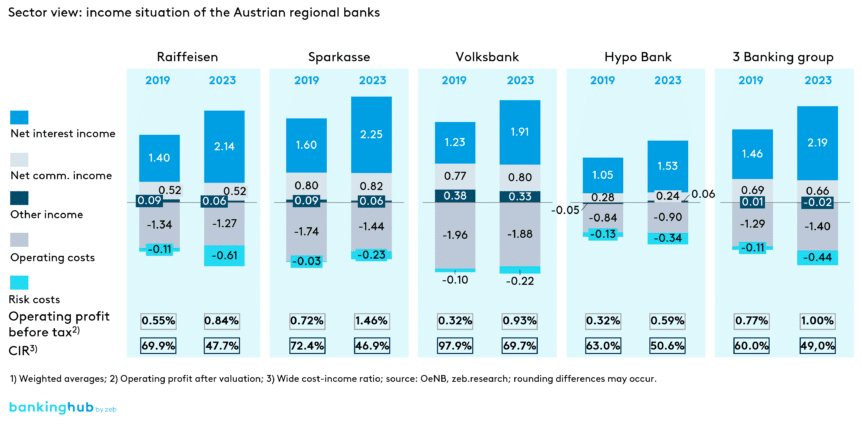
2023 was an exceptionally successful year for Austrian regional banks. The sharp rise in net interest income due to an increased interest rate level more than offsets inflation-related cost increases and rising risk costs, especially in commercial real estate development. All banking groups within the sector achieved significant growth in operating profit. A comparison of the years 2019 and 2023 shows: Sparkassen (savings banks) performed best, followed by the Volksbanken and Raiffeisenbanken (cooperative banks).
The strong increase in net interest income was driven by the high margin on deposits. Part of the rise in interest rates was not passed on to customers, a practice that can also be observed in other European countries such as Germany. In contrast to Germany, however, Austria’s banks benefit from a high proportion of variable loans. This allowed Austrian regional banks to gain more from the interest rate turnaround than their German counterparts.
How did the regional banks’ customer business develop?
Examining the regional banks’ on-balance sheet customer business reveals that deposit volumes grew by 18% between 2019 and 2023, while loan volumes increased by 19%. Growth in customer business was almost equal on both sides of the balance sheet.
However, there are clear differences between the sectors. In terms of market share, the Raiffeisenbanken still lead in both deposit and loan volumes, although the Sparkassen have gained market share in recent years, mainly due to strong deposit growth. All three types of banks experienced above-average deposit growth. On the lending side, the Raiffeisenbanken and Sparkassen outperformed the market average. The Volksbanken bring up the rear in terms of deposit and loan growth.
BankingHub-Newsletter
Analyses, articles and interviews about trends & innovation in banking delivered right to your inbox every 2-3 weeks
"(Required)" indicates required fields
What are the current economic and inflation perspectives?
All three types of banks experienced above-average deposit growth. Supported by base effects and falling energy costs, inflation targets should be within reach from 2025 onwards. Despite high uncertainty, the economy remains surprisingly robust given the tight monetary policy. After the recession year 2023, Austria’s economic output also fell by 1.1 % in 2024. Apart from public consumption, all other major components of GDP, such as exports, imports and investment, have declined.
The inversion of the yield curve was resolved in Austria in Q1 2025. Historically, this suggests that another recession is imminent, as recessions often begin after an inverted yield curve has un-inverted. There are also various (geo)political destabilizers. In addition to the armed conflicts, the faltering Franco-German engine of the EU due to national government crises and Donald Trump’s election victory in the US with unpredictable effects on tariffs, add to the challenges. In this challenging environment, banks are well advised to prepare for possible recession scenarios.
What are the study’s forecasts for the coming years?
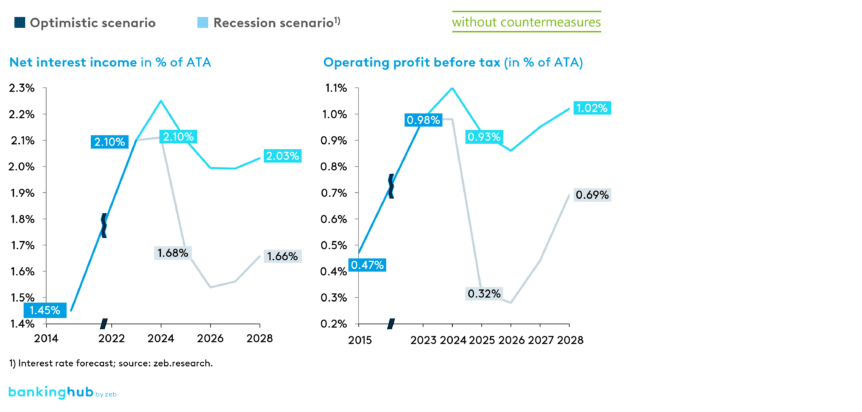
The simulation results of our study predict that Austrian regional banks could initially face another record year in 2024. Net interest income is expected to peak in that year. From 2025 onwards, we anticipate a deterioration in operating profit due to rising risk costs and a slight increase in operating expenses, coupled with falling net interest income.
- In the optimistic scenario, however, this implies a continued strong operating result of 1.0% of ATA in the years to 2028.
- In a recession scenario, an increase in bankruptcies combined with falling interest rates would lead to a significant decline in operating profit. The rising number of defaults on customer loans could increase the cost of risk, potentially leading to capital shortfalls for several regional banks in this scenario.
Which areas of activity are becoming important for Austrian regional banks?
- Market and income potential: Intelligent pricing and customer loyalty are key to securing a competitive advantage. With real growth close to zero in the coming years, banks need targeted action to secure revenue share.
- ESG: Integrating ESG into the business strategy presents both regulatory challenges and growth opportunities. Banks need to develop ESG KPIs to measure and monitor their ESG performance. Integrating ESG into risk management and reporting is critical to reducing systemic risk and promoting financial stability.
- NPLs and credit risks: The weak economy combined with higher interest rates and the catch-up effects of the pandemic are leading to an increase in the NPL ratio. This trend is expected to continue in the coming years. Banks’ restructuring and resolution units need to be prepared for future additional costs.
- Cost trends: Personnel and material costs have risen sharply since 2022, necessitating increased action. Increasing efficiency potential through standardization, economies of scale and digitalization is necessary to reduce cost pressure. The ratio of non-personnel costs to personnel costs will continue to rise in the future due to the need for investment, which will require a sustained transformation of business and operating models.
- Digital transformation: The future viability of financial institutions depends heavily on digital transformation. Innovation and increased efficiency are the key in this regard. An agile organization is necessary to ensure the required change environment.
- Personnel: Demographic change requires an active workforce strategy to meet the demand for highly skilled workers. By 2035, about 50% of today’s workforce will be gone due to demographics and attrition. Banks need to develop strategies to compensate for the decline in staff numbers. This will require measures to recruit, retain and develop staff.
- Artificial intelligence: AI is a key technology for the next stage of digital transformation and must be integrated individually for each industry. The use of AI provides a critical lever for digitizing tasks that were previously difficult to address. Banks need to develop and implement appropriate measures to integrate AI into their business processes. This includes optimizing customer interactions, increasing process efficiency, and improving the quality of decision-making.
Conclusion: What precautions should banks take in view of the uncertainties?
Austrian regional banks had a record year in 2023, driven by rising interest income. The overall medium-term outlook appears comfortable at first glance, but banks need to prepare for rising risk costs and operating expenses. The baseline simulation shows that the capital ratios of regional banks will increase slightly on average, further strengthening their currently comfortable capital situation.
However, given the (geo)political uncertainties and historical experience in the current interest rate environment, banks should not be too complacent. A recession scenario would mean a significant slump in operating profit. Such a scenario could lead to equity shortfalls for a large number of institutions. It is therefore advisable to plan and implement suitable measures at an early stage in order to be prepared for the potential challenges of the future.