How is a data-rich format transforming the world of financial messaging?
ISO 20022 is an international standard for financial messaging developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It provides a common framework for exchanging financial information across institutions, enabling consistent and structured data for payments, securities trade, and other financial transactions.
For decades, banks and financial institutions have relied on the SWIFT MT format – a rigid, text-based messaging standard that has served its purpose but is increasingly showing its age. ISO 20022 emerges as a direct response to the growing complexity and limitations of legacy messaging standards, replacing the SWIFT MT format[1] with the MX format[2], built on XML[3].
At its core, ISO 20022 is more than just a new messaging format – it’s a major leap in how financial institutions communicate. The MX messages are highly structured and allow for much richer, more detailed data to be transmitted with each transaction. For example, an XML message can include detailed information such as legal entity identifiers (LEIs), structured postal addresses, structured remittance details like invoice references, or specific roles identifying the ultimate debtor and creditor involved in a transaction.
In the short term, these enhanced capabilities translate into faster, more accurate transaction processing and simplified compliance through improved data transparency. Looking ahead, they support a strategic vision of a unified, efficient, and innovative global payments ecosystem.
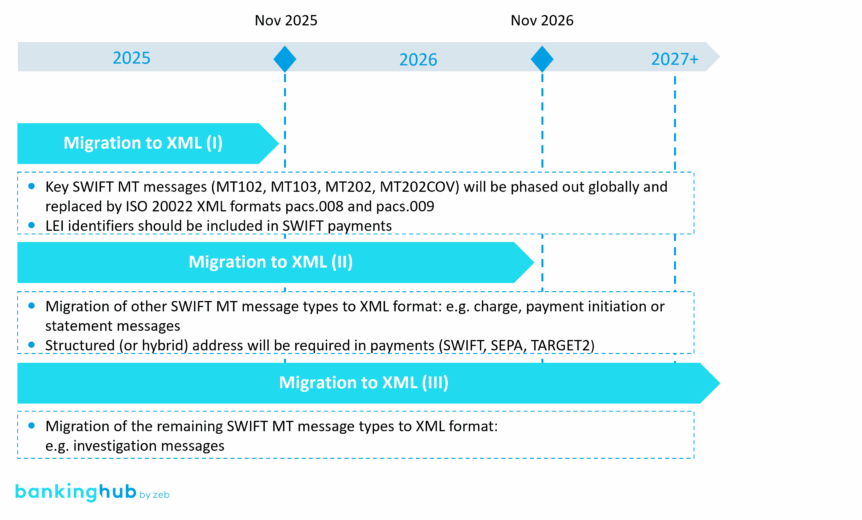
ISO 20022 is well underway, but not yet finished
The migration to ISO 20022 is already well advanced. SEPA and TARGET have already adopted the standard, but the transition will reach a significant milestone in November 2025 with the migration from SWIFT MT messages to XML. Core payment messages such as MT103 and MT202 will be replaced by richer ISO 20022 equivalents like pacs.008 and pacs.009.
However, this milestone does not mark the end of the implementation. To unlock the full benefits of ISO 20022, further changes are underway – and the next wave will come in 2026, when, for example, structured (or hybrid) addressing formats in payments become mandatory, supporting more efficient payment processing and enhancing the clarity and consistency of transaction data.
The next implementation stages are rapidly approaching
Payments and beyond
Although ISO 20022 primarily focuses on payment-related processes, its influence reaches far beyond core payment systems, impacting a wide range of internal bank functions that rely on payment data. From liquidity management and nostro reconciliation to trade finance, treasury, and KYC/AML, many areas can be affected – often in ways that are not immediately visible. Even downstream systems that rely on extracted payment data – for reporting, analytics, risk management, or customer insights – can be indirectly impacted, and assessing the full extent of these effects requires careful analysis and significant effort from the banks.
Convergence of schemes
At the same time, adaptation across schemes is not uniform. ISO 20022 provides a common standard, but different payment schemes are not always adapted to ISO in the same way. For example, SWIFT has introduced structured fields for remittance information, allowing detailed payment data to be captured in separate fields, while SEPA relies on a limited format, often combining multiple pieces of information into a single field. In practice, this makes ISO 20022 not just a one-time migration, but a continuous effort between systems to harmonize payments globally and make cross-border transactions more consistent and efficient.
BankingHub-Newsletter
Analyses, articles and interviews about trends & innovation in banking delivered right to your inbox every 2-3 weeks
"(Required)" indicates required fields
Why is doing the bare minimum not good enough?
As ISO 20022 adoption progresses, many banks have chosen a “minimalistic” approach to implementation. In practice, this translates into relying on message conversions rather than redesigning the end-to-end payment flows. Two main types of conversions are commonly applied: MX to MT conversion at the initial stage of incoming payments processing and MT to MX conversion at the final stage of outgoing payments processing.
This strategy allows institutions to remain compliant with regulatory timelines while avoiding disruptive system overhauls, often not feasible in case of legacy systems. However, it also creates an additional layer of complexity. Maintaining dual formats throughout the payment life cycle can lead to data loss during conversion, inconsistent customer reporting, and increased operational complexity.
From this perspective, the main issues fall into two areas:
1) Customer experience
Minimalistic implementations can affect the customer experience at both ends of the payment process. On the initiation side, customers might be required to continue using legacy MT formats when submitting transactions (with the bank converting them into MX internally at a later stage), which prevents them from capturing the richer data elements enabled by ISO 20022, such as structured remittance information or extended party details. On the reporting side, much of the additional information carried in ISO 20022 messages could be truncated in the conversion to MT format and therefore not available in account statements and reporting tools. Bridging these gaps requires significant IT updates, enhanced workflows, and careful field mapping to ensure customers can leverage the full value of ISO 20022.
2) Data quality
From an operational perspective, maintaining accurate and complete data becomes increasingly challenging when multiple conversions occur throughout the payment flows. Converting incoming MX messages to MT too early risks losing critical details before they reach internal systems, while transforming outgoing MT messages back to MX can further complicate reporting, reconciliation, and compliance processes. Each conversion introduces a risk of information loss or misalignment, forcing banks to implement additional mapping, validation, and monitoring procedures to safeguard data integrity – an effort that can make internal operations considerably more complex.
Taken together, these issues show that while minimalistic adoption may be sufficient for short-term compliance, it does not unlock the full potential of ISO 20022. To ensure that there is no payment data loss from both the customer and the internal processes perspective, banks will need to move beyond conversion tactics and embrace more integrated, long-term solutions.
In what ways is ISO 20022 a catalyst for transformation?
Although financial institutions are currently focused on meeting regulatory requirements, ISO 20022 brings a wide range of benefits related to message processing and management. By introducing rich, structured, and standardized message formats, it allows financial institutions to unlock new levels of automation, accuracy, and insight.
The potential uses of enhanced data can be broadly categorized into four key benefit areas:
Excursus: What is the role of AI in unlocking the full potential of ISO 20022?
As banks implement the new ISO 20022 data standard, layering artificial intelligence on top of its structured messaging unlocks the next level of insight – transforming standardized information into true intelligence that can anticipate trends, detect anomalies, and optimize payment flows end-to-end.
For instance, AI trained on structured data can automatically spot inconsistencies in remittance details before payments are processed, preventing costly delays. In compliance and risk management, machine-learning algorithms analyzing message fields are able to detect subtle fraud patterns that traditional rule-based systems might miss. Additionally, AI can optimize payment routing in real time, selecting the fastest and most cost-efficient paths based on transaction characteristics.
These examples illustrate just a fraction of AI’s potential, yet the synergy between ISO 20022’s structured data and AI’s analytical power effectively transforms compliance into strategy. Once ISO 20022 is fully integrated, banks hold “data-rich” payment ecosystems that AI can continuously learn from – analyzing which corridors are high-cost, where STP failures occur, or where new products and rails could be introduced.
Ultimately, ISO 20022 and AI are complementary forces: one provides clarity and structure, the other delivers intelligence and speed. Together, they transform payments from a regulatory upgrade into a catalyst for innovation and growth
Our zeb Maturity Check – a holistic approach to ISO 20022 readiness
With deep industry knowledge and hands-on ISO 20022 implementation experience, zeb helps financial institutions navigate this complex transition. Our ISO 20022 Maturity Check is designed to assess the readiness and potential of a bank across multiple dimensions, including payment processing, data utilization, and process optimization. It identifies opportunities where structured and enriched payment data can add tangible value, helping institutions align their ISO 20022 adoptions with broader business goals.
ISO 20022 Maturity Check – key focus areas
- Adoption and utilization assessment – it evaluates how the ISO 20022 format is being applied across the bank’s business processes and identifies areas where usage can be improved to unlock its full potential
- Readiness vs. planned approach – it examines the preparedness of impacted areas in relation to the bank’s planned implementation strategy, highlighting gaps and opportunities for alignment
- Potential for value creation – it identifies business processes that can benefit from structured and enriched payment data, enabling operational improvements and strategic advantages
By focusing on maturity rather than just compliance, banks can ensure that the adoption of ISO 20022 translates into operational efficiency, better decision-making, and long-term strategic advantage in an increasingly data-driven financial ecosystem.
Our Maturity Check can provide the insight and direction needed to navigate the transition with confidence, ensuring your institution will be best positioned to unlock the full potential of ISO 20022 and capitalize on strategic opportunities ahead.