Why is strategic management necessary now?
These developments entail various requirements that must be addressed as part of HR management: retirements, shifting career spans, increased job mobility, and new skill profiles driven by digitalization and automation. At the same time, many institutions lack consistent data, realistic planning parameters and clearly defined responsibilities.
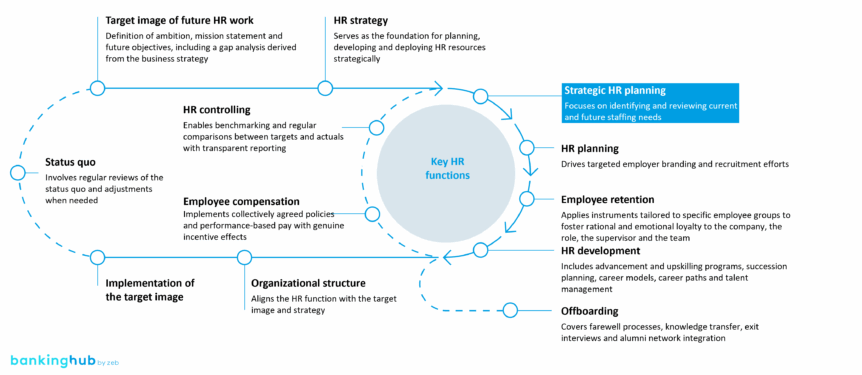
Strategic HR planning provides transparency regarding current staffing, future needs and scenarios. It enables data-driven management of the company’s most important resource – its workforce. Only those who understand where, when and with which qualifications employees are needed can build up, develop and restructure staff effectively.
Strategic HR planning forms an integral part of the HR management cycle. It translates business strategy requirements into actionable HR processes such as recruitment, retention and employee development. This ensures that strategic goals are not only defined but can also be implemented through targeted staffing measures.
What four phases serve to secure the future in HR planning?
A proven method for strategic HR planning consists of four phases.
I) Status quo and consolidation
The first phase of strategic HR planning involves building a consolidated, reliable database that serves as the foundation for all simulations and analyses and determines the quality of future management decisions.
The status quo is usually assessed using the bank’s current staffing plan with actual and target allocations by area, the HR forecast with relevant parameters, such as attrition assumptions, and zeb’s criteria catalog for target staffing plans. The consolidation process follows clearly defined steps. First, employee characteristics and counting methods, such as how to account for trainees, partial retirement and long-term illness to ensure comparability, are established jointly to ensure comparability. Next, the staffing plan is evaluated by relevant segments such as area, role and age group. In addition, the actual full time equivalents (FTE) are compared with the target to identify any surplus or shortage. At the end of this phase, three key outcomes emerge:
At the end of this phase, three key outcomes emerge:
- Standardized definitions of employees and relevant attributes
- A coordinated catalog of requirements for subsequent planning
- An up-to-date overview of employees as of the reporting date, including a comparison with target figures
This consolidated baseline enables reliable simulations of headcount (FTE) and staffing needs and lays the groundwork for data-driven, strategically aligned HR management.
BankingHub-Newsletter
Analyses, articles and interviews about trends & innovation in banking delivered right to your inbox every 2-3 weeks
"(Required)" indicates required fields
II) Simulation of workforce development (“Gap 1.0”)
Following the consolidation of the status quo, the next phase focuses on simulating future workforce development. The goal is to create transparency regarding potential gaps using realistic assumptions and scenarios, broken down by department, age group and role.
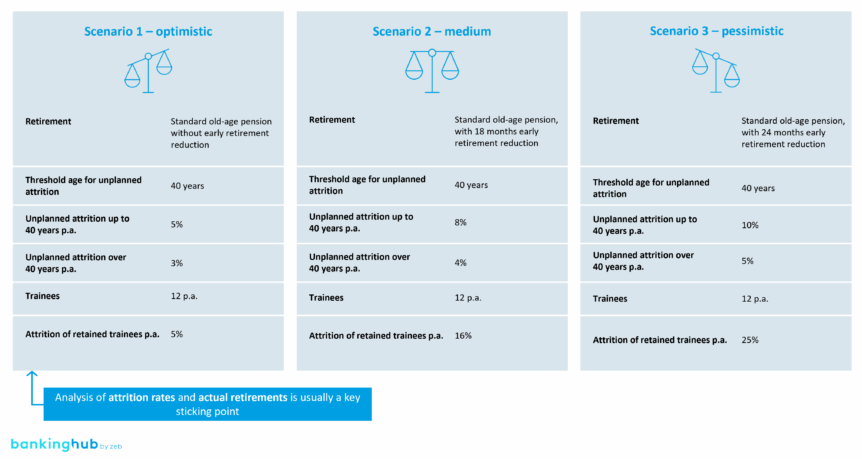
zeb uses a proprietary tool to simulate workforce development, external benchmarks for age-specific attrition and retirements, and the consolidated data from phase 1, such as staffing plans and attrition assumptions.
The simulation follows a structured process that begins with identifying key drivers and sensitivities of future development – such as attrition by age group, lead times for replacements and inflows from trainee retention. Scenarios are then set up with varying driver intensities, and a time horizon for the simulation is defined, typically spanning five or ten years. Using the zeb tool, simulations are conducted to project workforce development and highlight specific gaps compared to the status quo (“Gap 1.0”).
At the end of this phase, the following outcomes are achieved:
- Ability to simulate workforce development
- Transparency regarding future workforce trends
- Identification of staffing gaps
III) Simulation of staffing needs (“Gap 2.0”)
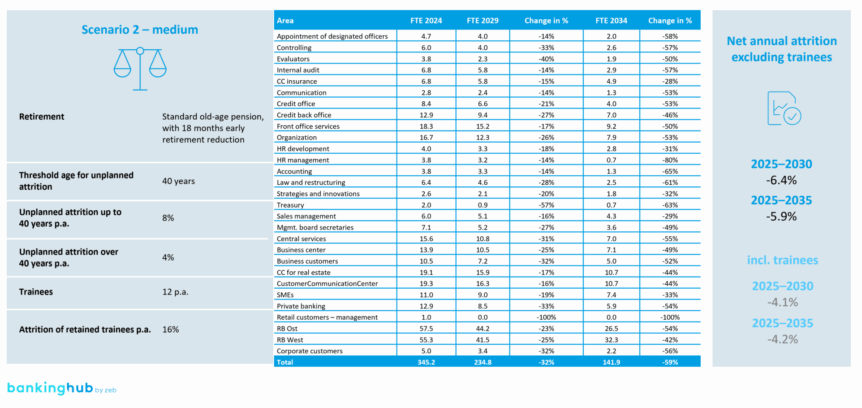
Building on the simulation of workforce development, the next step is to determine future workforce requirements. The goal is to translate requirements from medium-term planning and strategic development into concrete staffing needs and to identify areas for action.
The results of the workforce development simulation (“Gap 1.0”), the customizable zeb simulation tool as well as strategic and operational data from the company’s medium-term planning serve as input. Core activities include jointly evaluating strategic developments, defining key assumptions for medium-term planning for existing and new business, customizing the zeb simulation tool and running simulations on staffing trends.
In addition, the simulation identifies specific gaps between available FTE and staffing requirements (“Gap 2.0”) and highlights areas for action such as restructuring, training and recruitment, which are allocated preliminary priorities.
The main outcomes of this phase are:
- Ability to simulate staffing needs within the framework of medium-term planning
- Validated staffing requirements, especially from bottom-up planning
- A preliminary prioritization of strategic areas for action
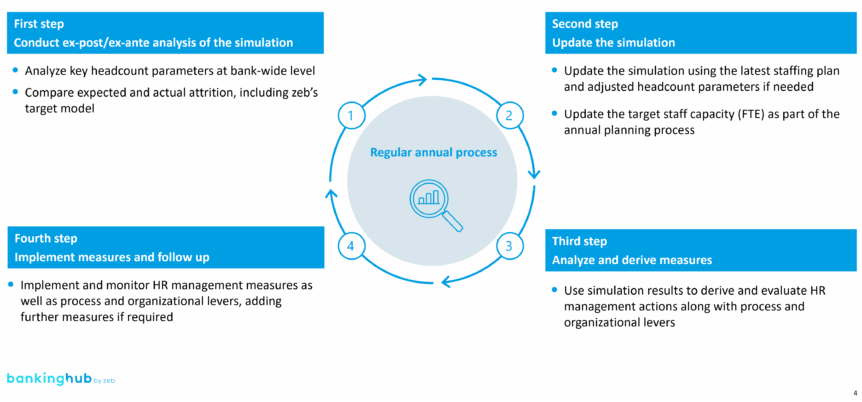
IV) Integration with the regular process
Strategic HR planning reaches full effectiveness only when integrated into the regular annual HR planning process. The goal is to permanently embed the developed structures and insights.
The regular HR planning process serves as input. Core activities include identifying parameters that require future additions or adjustments, reviewing and refining responsibilities and competencies in the regular annual planning process. These steps are followed by validating alignment with existing resources and tools and documenting the updated process in a results report.
The main outcomes are:
- An enhanced regular process with clearly defined responsibilities
- Validated requirements for tools and processes
- Documented results as a foundation for annual updates
What challenges and levers are there in strategic HR planning?
The analysis reveals frequent gaps in consistent data, realistic planning parameters and clearly defined responsibilities. Knowledge silos, inconsistent attrition assumptions and limited simulation capabilities hinder effective HR management.
At the same time, strategic HR planning offers powerful levers:
- Early identification of fields of action
- Qualification strategies for long-serving employees
- Realistic scenarios for restructuring and recruitment
- Integration into overall strategic planning
Conclusion: strategic foresight outperforms short-term reactions
Strategic HR planning is not an end in itself. It is a prerequisite for forward-looking HR management and, by extension, for the organization’s overall ability to act. Savings banks and cooperative banks that take action today won’t need to react tomorrow.
Those who see their workforce as a strategic success factor not only gain stability but also secure their future.