How does automation using AI work?
The capabilities of intelligent process automation are different from traditional process automation in that they can process unstructured data by using learning-based methods. In this type of process automation, so-called machine learning algorithms are applied to source data, detect patterns there, abstract from them and predict an associated output based on new input data. This prediction can already be the final output in the process (e.g. tagging a customer inquiry with a keyword) or the output can be fed into a next process step (e.g. subsequently routing the customer inquiry to the appropriate employee).
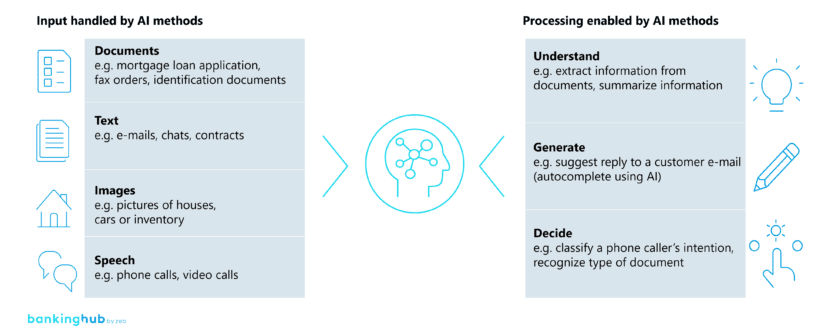
In the banking environment, unstructured data of the following categories is particularly common: documents (e.g. mortgage loan application, fax orders, identification documents), text (e.g. e-mails, chats, contracts), images (e.g. pictures of houses or inventory) and speech (e.g. phone calls).
Basically, there are three processing options for unstructured data using AI in the context of process automation:
- Understand – e.g. extract and summarize information contained in documents
- Generate – e.g. suggest a reply to a customer inquiry
- Decide – e.g. classify the intention of a customer inquiry
What are the application areas of intelligent automation in the banking environment?
Often it is areas that produce large numbers of documents that have the highest automation potential. One example is the provision of banking products (including authentication) for new customers. However, due to the huge differences in business models and the already prevailing degrees of automation in banks and financial services providers, it is not possible to generalize the application areas for using intelligent process automation.
A potential analysis helps to create transparency. Where can efficiencies be leveraged? Where can service availability be increased and error rates reduced?
Potential advantages should always be evaluated in light of the bank’s strategic orientation.
Different approaches can be used to identify and verify automation potential. Options include hypothesis-based approaches, expert interviews, conducting a process assessment or even using analytical tools (e.g. process mining).
Status quo of process automation – what is current practice in the market?
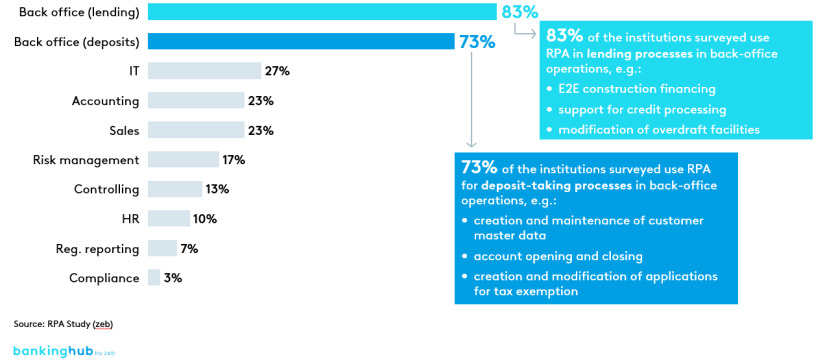
On the one hand, traditional process automation, for example RPA, is already used across the board in the German financial services industry – at over 80% of all institutions, according to the zeb.RPA study.
However, coverage varies widely between the different areas of a bank. While 83% of the institutions use RPA in back office functions for lending business, only 7% use it for regulatory reporting. Here, RPA can be used to automatically correct reporting documents, for example.
In order to best leverage efficiency potential through RPA, it is therefore necessary to better integrate different areas of a bank or to have a bank-wide mandate from the board of directors.
On the other hand, intelligent process automation by means of AI is still in its infancy. Most banks and financial services providers consider AI to be strategically important and perceive process automation to be one of the most important uses of AI. Nevertheless, there have been few successful implementations to date, even though there are many promising use cases (e.g. automatic document processing).The reason for this lies in the frequent lack of skills to evaluate and implement AI use cases.
This issue can be solved with the help of competent partners who implement AI use cases and purposely pass on knowledge to the bank’s employees. In addition, development costs are higher for AI use cases than for RPA implementations. Therefore, the question of which AIs are to be developed in-house and which should preferably be purchased needs a great deal of consideration. Here, too, a partner with a good overview of the market can be a big help.
Institutions that take the time to learn process automation through AI will have a competitive advantage as early movers. Are you one of them?